We believe in the daily life, you must be in constant contact with motor, this article we want to give you some knowledge about it.
What Is A Motor?
Motor (commonly known as “electric motor”) is a kind of electromagnetic device which achieves the conversion or transmission of electric energy according to the law of electromagnetic induction. Its main function is to generate driving torque as the power source of electrical appliances or all kinds of machinery.
The main function of motor is to convert electric energy into mechanical energy.
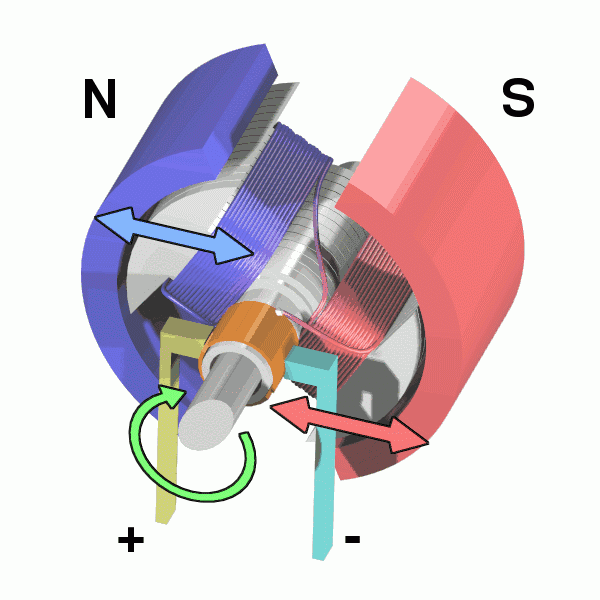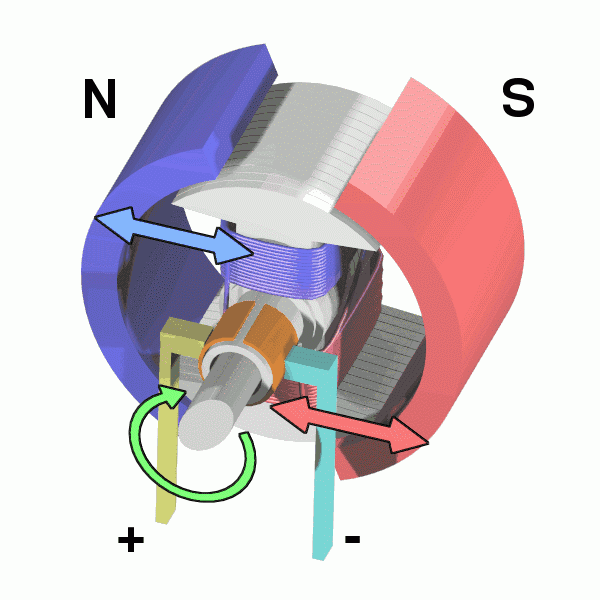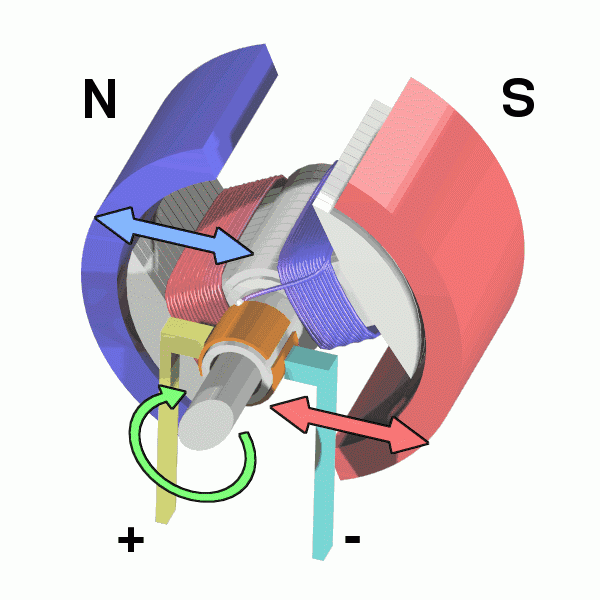
The motor mainly consists of an electromagnet winding (or distributed stator winding) and a rotating armature (or rotor), and other accessories.
Under the action of the rotating magnetic field of the stator winding, the current passes through the armature squirrel cage aluminum frame and rotates under the action of the magnetic field.
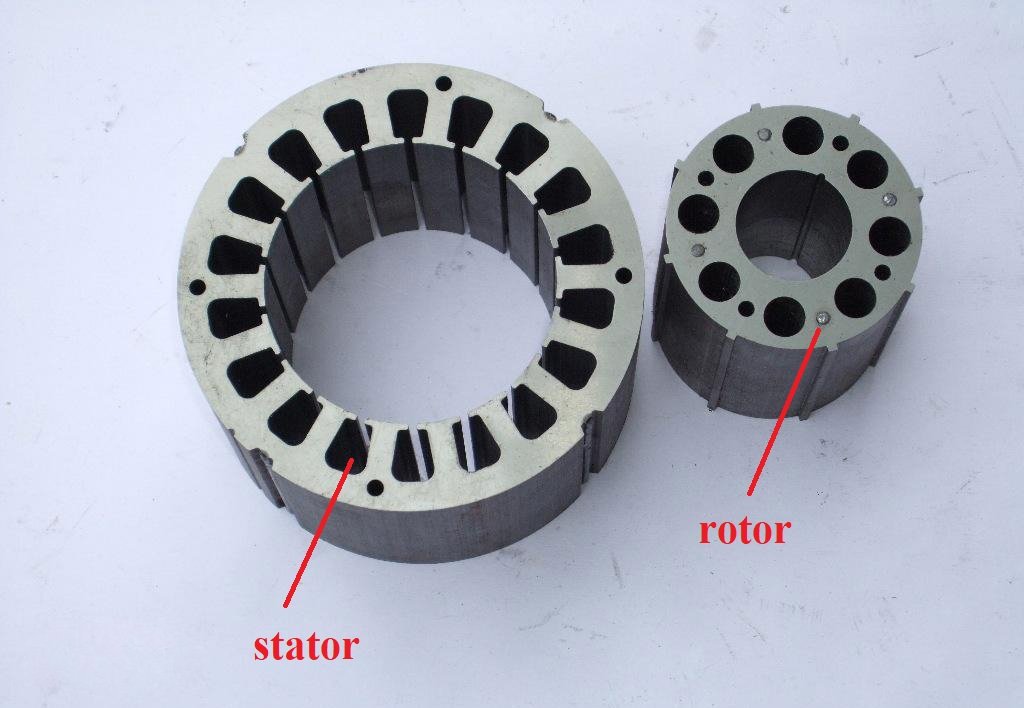
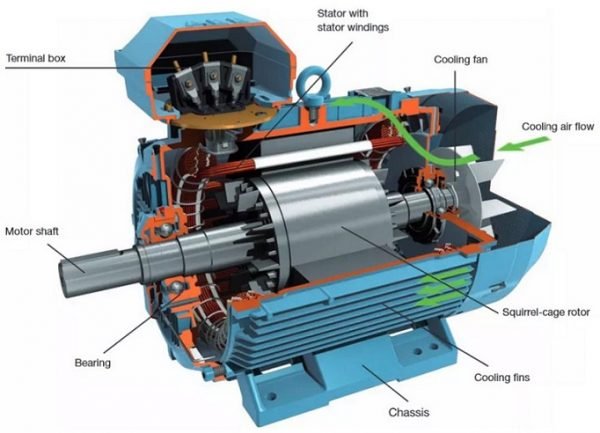
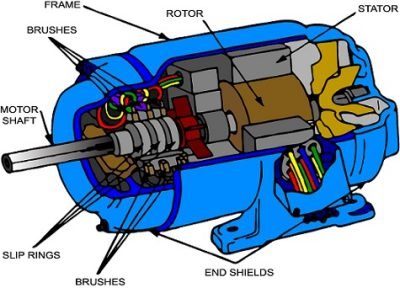
Stator (Stationary Part)
Stator core: part of the magnetic circuit of a motor, on which stator windings are placed.
Stator winding: the circuit part of a motor that connects to alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Machine base (chassis): fix the stator core, the front, and rear end cover, to support the rotor. Play the role of protection, heat dissipation, and so on.
Rotor (Rotating Part)
Rotor core: as part of the magnetic circuit of the motor and placing the rotor winding in the core slot.
Rotor winding: cutting the rotating magnetic field of the stator, producing induced electromotive force and current, then forms electromagnetic torque to make the motor rotate.
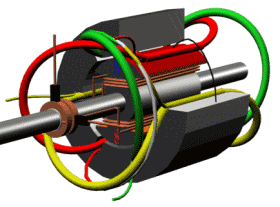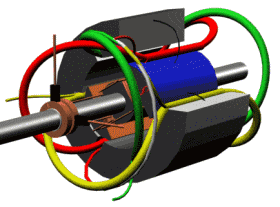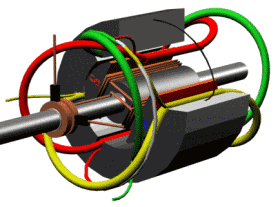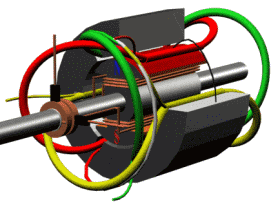
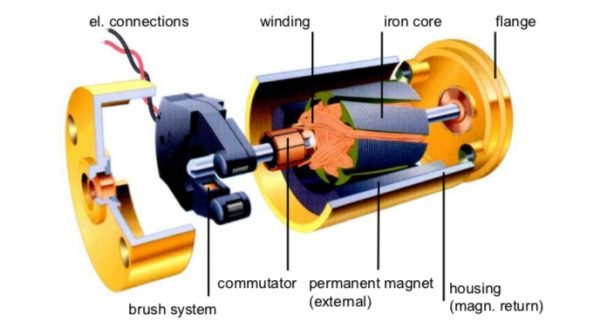
Motor running diagram
Stator and rotor (for fan motor)
Motor section view
What Is Carbon Brush?
Carbon brushes are also called electric brushes.
They are mainly used in electrical equipment, used to transmit signals or energy between the fixed and rotating parts of some motors or generators. Its shape is rectangular, in the spring installed metal wire. Because it is a kind of sliding contact, easily worn and needs to replace and clean regularly.
The main component of a carbon brush (main material is graphite) is carbon, when pressed by a spring, the carbon brush will work likes a brush onto the rotated parts, so that is why called carbon brush.
Carbon brush
What Is A Brushed Motor?
When the motor is working, the coil and commutator rotate, but the magnetic steel and carbon brushes don’t rotate. The alternating current direction of the coil is changed by the commutator and brushes that rotate with the motor.
In the electric vehicle industry, brush motors can divide into two types: high-speed brush motor and low-speed brush motor.
Simple differences of both as: brush motor has carbon brushes, but the brushless motor doesn’t have carbon brushes.
Classification of Daily Used Motor
1. Permanent Magnet Motor
Permanent magnet motor uses a permanent magnet to provide a magnetic field.
There are two conditions for a motor to do work: one is the existence of a magnetic field, the other is the existence of a moving current in the magnetic field.
Permanent magnet motor
Permanent magnet
2. DC Motor
A DC motor is a rotating motor that converts DC electrical energy into mechanical energy (DC motor) or mechanical energy into DC electric energy (DC generator).
It is a motor that can achieve the conversion between DC electric energy and mechanical energy.
DC motor
DC motor structure
Usage: DC motors are generally used in circuits with low voltage requirements. DC power supplies can easily carry. For example, electric bicycles, computer fans, and radios all use DC motors.
DC motors are used as power to drive various production machinery to work and output mechanical energy to the load. In the control system, DC motors have other uses as well, such as speed motors, servo motors, etc.
Although the purposes of DC generators and DC motors are different, their structures are basically the same: both use the interaction of electricity and magnetism to realize the mutual conversion of mechanical energy and electrical energy.
3. Unidirectional Asynchronous Motor
Induction motor
Asynchronous motor, also known as induction motor, is a kind of AC motor that produces electromagnetic torque by the interaction between air gap rotating magnetic field and rotor winding induced current, so as to convert electromechanical energy into mechanical energy.
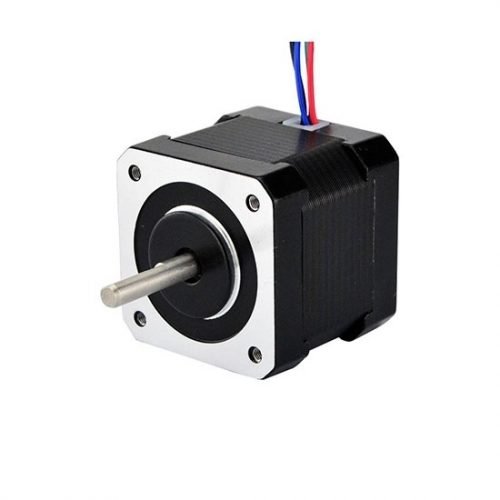
4. Stepper Motor
Stepper motor is an open-loop control element which converts the electric pulse signal into angular displacement or linear displacement.
Stepper motor
In the case of non-overload, the speed and stop position of the motor only depend on the frequency and pulses’ number of the pulse signal, meanwhile aren’t affected by the change of the load. When the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate at a fixed angle in the set direction.
Controlling the number of pulses to achieve the control of angular displacement, so as to achieve the aim of accurate positioning; at the same time, controlling pulse frequency to dominate speed and acceleration of motor rotation, in order to achieve the purpose of speed regulation.
The working principle of stepper motor:
When the current flows through the stator winding, the stator winding produces a vector magnetic field.
The magnetic field will drive the rotor to rotate an angle so that the direction of the pair of magnetic fields of the rotor is consistent with that of the stator.
When the vector magnetic field of the stator rotates at an angle.
The rotor also rotates at an angle with the magnetic field.
With each input of an electric pulse, the motor rotates at an angle and takes a step forward.
The angular displacement of its output is proportional to the number of input pulses and the rotational speed is proportional to the pulse frequency.
Change the order in which the windings are electrified, and the motor will reverse.
Therefore, the rotation of the stepper motor can be controlled by the number and frequency of control pulses and the power-up sequence of each phase winding of the motor.
Tips: The following video will show how the stepper motor works.
The Differences Of Motor
1. The Difference Between DC and AC Motor
As the name implies, DC motors use DC as a power supply, and AC motor uses AC electricity as the power supply.
In structure, the principle of DC motor is relatively simple, but its structure is complex and isn’t easy to maintain.
The principle of an AC motor is complex, but its structure is relatively simple, and it is easier to maintain than a DC motor.
For the price, DC motor with the same power is higher than AC motor, including the speed control device, the DC speed regulation device are both higher than that of the AC speed regulation device.
For the performance, because the speed of DC motor is stable and the speed control is accurate, which can’t be achieved by AC motor.So in industries that have strict speed requirements, we have to use the DC motor instead of AC motor.
2. The Difference Between Synchronous Motor and Asynchronous Motor
1) Motor synchronization difference
Synchronous motor speed and electromagnetic speed synchronization, while the speed of the asynchronous motor is lower than the electromagnetic speed, synchronous motor regardless of the size of the load, as long as not out of step, the speed will not change, the speed of the asynchronous motor always follow the changes in the size of the load and change.
2) Structure differences
Synchronous motor has high precision, but complex construction, high cost, and relatively difficult maintenance.
While asynchronous motor has slow response, but easy to install and use, and cheap as well. So synchronous motor is not widely used than asynchronous motor.
Synchronous motor structure
3) The difference of using occasions
Synchronous motors are mostly used in large generators, while asynchronous motors are almost used in electric motors.
4) Main difference
Synchronous motor and asynchronous motor are with or without slip (the difference between magnetic field speed and rotor speed)
5) Different rotor structure
The rotor of the synchronous motor is a magnetic pole (permanent magnet or adding DC excitation current); the rotor of the asynchronous motor is a closed winding. The main applications of synchronous motors are in generators. The asynchronous motors are used in electric fans, washing machines, and refrigerators, etc, in daily life you will see them frequently.
6) Different working principle
Synchronous motor uses the principle of: rotor poles and stator rotating magnetic field of opposites attracting and same-sex repelling to produce electromagnetic torque; asynchronous motor uses the stator rotating magnetic field to cut the rotor winding to make the rotor produce induced electric potential and induced current, and use amperage to produce electromagnetic torque.
7) Different working speed
The synchronous motor can have electromagnetic torque only when the rotor speed is “equal” to the stator rotating magnetic field speed; the asynchronous motor can have electromagnetic torque only when the rotor speed is “not equal” to the stator rotating magnetic field speed.
3. The Difference Between Ordinary and Inverter Motor
First of all, an ordinary motor can’t be used as inverter motor.
The ordinary motor is designed by constant frequency and constant voltage, it can’t be fully adapted to the requirements of inverter speed regulation, so it can’t be used more as an inverter motor.
How to distinguish between ordinary motor and inverter motor?
1) Higher insulation level requirements
Generally, the insulation level of inverter motor is F or higher, to strengthen the insulation to ground and the strength of the wire-turn insulation, especially to consider the ability of insulation to withstand shock voltage.
2) The vibration and noise requirements of inverter motor are higher
Inverter motor should fully consider the rigidity of motor components and the whole, and try to improve its inherent frequency to avoid resonance with each force wave.
3) Different cooling methods of inverter motor
Inverter motor generally adopts forced ventilation cooling, that is, the main motor cooling fan is driven by an independent motor.
4) Different requirements of protection measures
Bearing insulation method should be adopted for inverter motors with a capacity over 160KW.
For a constant power inverter motor, when the speed exceeds 3000/min, special grease with high-temperature resistance should be used to compensate for the temperature rise of the bearing.
5) Different heat dissipation system
Inverter motor cooling fan adopts an independent power supply to ensure continuous cooling capacity.
Conclusion
From the above content, we have a basic understanding of motors and common motor problems.
In fact, we have to contact motors every day in our daily lives, just you have not paid attention to it. Such as electric shaver, computer, washing machine, dishwasher, etc.
So it is very useful for us to understand some basic knowledge about motors.
Any comments?
Welcome leave a message or repost.