One-Stop OEM & ODM Solution Partner
We produce Tri-phase electric motor 0.1 ~400Kw, 2/4/6/8/10 Poles, 220/ 380/ 440/ 660/ 690 Volt, both 50 and 60Hz, also can customize due to your unique requirement and drawing. Quality is guaranteed, contact us freely NOW.
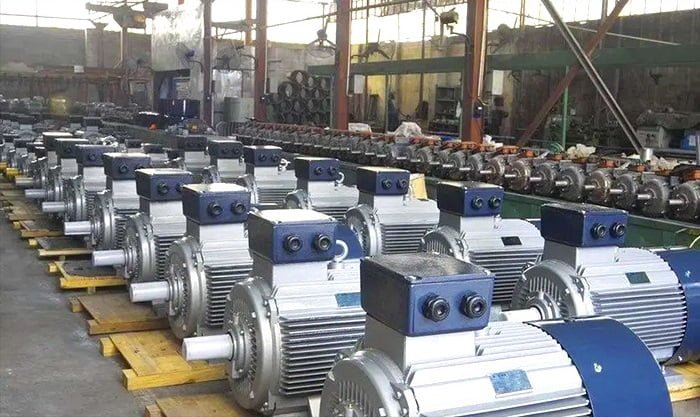

Electric motor is a device converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field.
“Speedway” manufactures electric motor since 2015, has Y,YE, IE, YD, MS, YVP, YCT, YC, YL series,etc, focus on exporting to more than 70 different countries and areas, we know your market and how to solve your issue.
With a focus on technological advancement and customer satisfaction, China Speedway Group continues to evolve and expand its offerings in the electric motor industry.
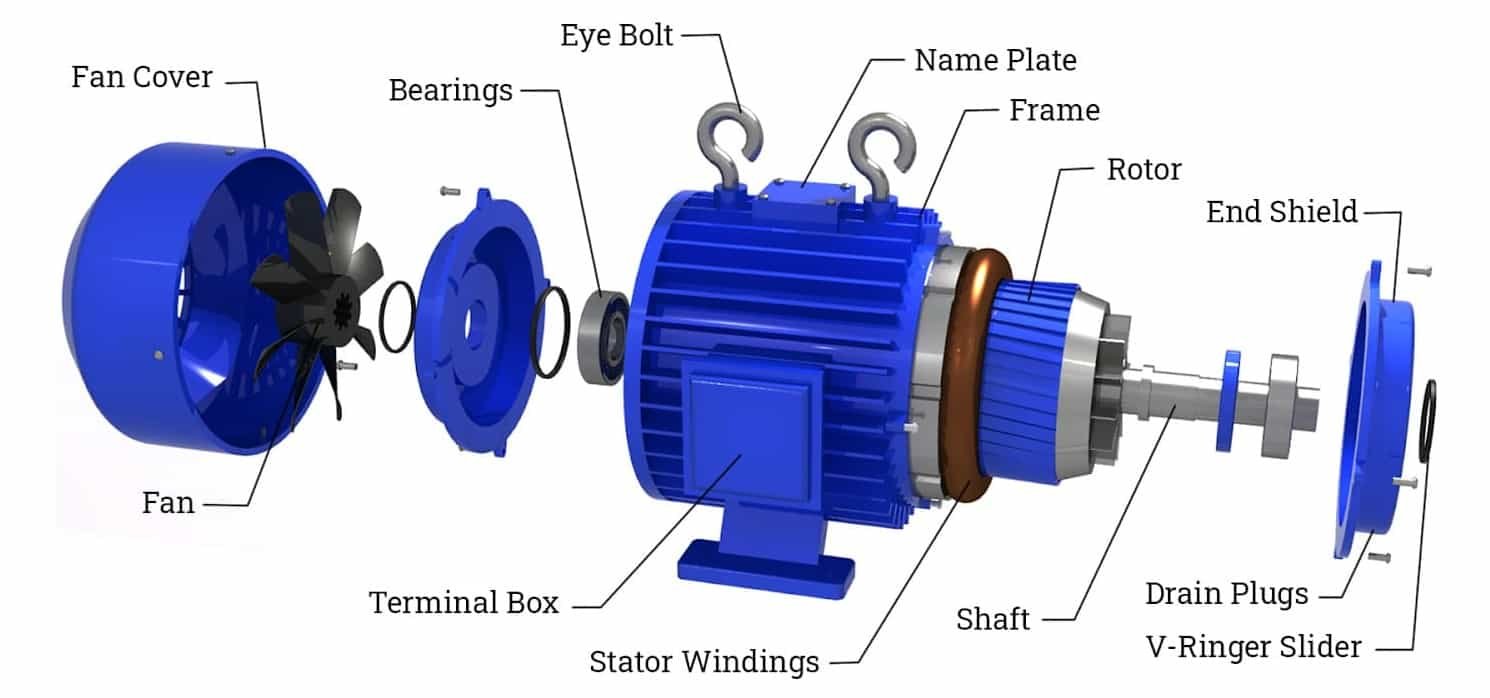
#1.DC Motors
1) Brushed DC Motor
Use brushes and a commutator to switch the current direction in the armature windings, resulting in continuous rotation.
DC means “Direct-Current”.
2) Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Also known as electronically commutated motors, these motors use electronic controllers to switch the stator windings, eliminating the need for brushes.

#2. AC Motors
1) Asynchronous motor
The most common type of AC (Alternating-Current) motor where the rotor is driven by electromagnetic induction without any electrical connections to it.
1.1) Single-Phase Asynchronous motor
Used in smaller applications and require a starting mechanism.
1.2) Three-Phase Asynchronous motor
Efficient and robust motors used in industrial applications.

2) Synchronous Motor
These motors rotate at a speed synchronized with the frequency of the AC supply. They can be synchronous reluctance motors or permanent magnet synchronous motors.
#3. Special Motors
1) Stepper Motor
Used in precise motion control applications, stepper motors move in discrete steps.
2) Servo Motor
Can precisely control angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration.
3) Linear Motor
These motors produce linear motion directly without the need for rotary-to-linear conversion mechanisms.
4) Hermetic Motor
Sealed motors used in applications where prevention of external contamination is critical, such as refrigeration compressors.
| Faults | Reason | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Fails to Start | 1. Faulty power supply | 1. Check power source and connections. |
| 2. Faulty motor windings | 2. Test windings for continuity or shorts. | |
| 3. Overload or thermal protection engaged | 3. Allow motor to cool, reset thermal overload if necessary. | |
| Motor Overheating | 1. High ambient temperature | 1. Improve ventilation around motor. |
| 2. Overload or excessive duty cycle | 2. Reduce load or verify motor is appropriately sized. | |
| 3. Insufficient cooling | 3. Clean air vents, ensure fan is functioning. | |
| Motor Runs but No Output | 1. Mechanical failure (e.g: broken rotor, damaged couplings) | 1. Inspect mechanical components, replace as needed. |
| 2. Open electrical connections | 2. Check and tighten all electrical connections. | |
| 3. Faulty starting components (capacitor, switch) | 3. Test and replace faulty components. | |
| Motor Runs at Inconsistent Speed | 1. Voltage fluctuations | 1. Stabilize voltage supply with regulators or UPS. |
| 2. Faulty speed control devices (VFDs, controllers) | 2. Inspect and calibrate speed control devices. | |
| 3. Mechanical load variations | 3. Check load conditions and adjust as needed. | |
| Motor Produces Unusual Noises | 1. Loose or worn mechanical parts | 1. Tighten or replace loose/worn parts (e.g: belts, couplings). |
| 2. Broken rotor bars or stator laminations | 2. Inspect rotor and stator for damage, repair or replace if needed. | |
| 3. Cavitation in pumps (if applicable) | 3. Check fluid levels and pump operation. | |
| Motor Vibrates Excessively | 1. Improper mounting or foundation | 1. Ensure motor is securely mounted on a stable foundation. |
| 2. Rotor imbalance | 2. Balance the rotor or replace damaged components. | |
| 3. Worn or damaged bearings | 3. Inspect and replace worn bearings. | |
| 4. Electrical issues (e.g: phase imbalance) | 4. Check for balanced electrical phases. | |
| Motor Frequent Tripping | 1. Overload or short circuit conditions | 1. Test motor windings for shorts and verify load conditions. |
| 2. Faulty protective devices (overload relays, circuit breakers) | 2. Inspect and calibrate protective devices. | |
| 3. External factors (e.g., power surges, lightning strikes) | 3. Install surge protectors or lightning arresters. | |
| Motor Exhibits Electrical Sparks | 1. Worn brushes or commutator | 1. Replace brushes or refurbish commutator. |
| 2. Contamination or moisture in electrical components | 2. Clean and dry affected components thoroughly. | |
| Motor Experiences Frequent Bearing Failures | 1. Improper lubrication | 1. Ensure bearings are adequately lubricated as per manufacturer’s guidelines. |
| 2. Contamination (dust, moisture) | 2. Protect motor from contaminants; use seals if necessary. | |
| 3. Misalignment or excessive vibration | 3. Check alignment and balance; correct as needed. | |
| Motor Brushes Wear Out Quickly | 1. Excessive current flow through brushes | 1. Check motor load and voltage; ensure they are within specifications. Replace brushes with correct type and size. |
| 2. Poor brush contact with commutator | 2. Clean or replace brushes; ensure proper seating and tension. | |
| 3. Contaminants or debris on commutator | 3. Clean commutator surface thoroughly. | |
| Motor Stalls or Loses Torque Under Load | 1. Insufficient power supply voltage or current | 1. Check voltage levels under load conditions; address any issues with power supply. |
| 2. High mechanical load beyond motor rating | 2. Evaluate load conditions and ensure motor is appropriately sized. | |
| 3. Worn or damaged bearings | 3. Replace worn bearings; inspect for shaft misalignment. | |
| Motor Corrosion or Rust | 1. Exposure to moisture or corrosive environments | 1. Protect motor with suitable coatings or enclosures. |
| 2. Improper storage or maintenance practices | 2. Store motor in dry, controlled environment; conduct regular maintenance. | |
| Motor Develops Excessive Shaft Play | 1. Worn bearings or bushings | 1. Replace worn bearings or bushings with correct replacements. |
| 2. Shaft misalignment | 2. Check and correct shaft alignment using precision tools. | |
| 3. Excessive axial or radial loads | 3. Verify loads on shaft; consider redesigning support structure. | |
| Motor Shaft Seizes or Locks Up | 1. Lack of lubrication or using incorrect lubricant | 1. Ensure proper lubrication with recommended oil or grease. |
| 2. Excessive dirt or debris within motor | 2. Clean motor interior; protect against contaminants. | |
| 3. Overheating due to excessive load or ambient temperature | 3. Reduce load; improve cooling around motor. | |
| Motor Runs in Reverse Direction | 1. Incorrect phase sequence in supply voltage | 1. Verify and correct phase sequence at motor terminals. |
| 2. Faulty or miswired control circuit | 2. Check control wiring and connections; correct as needed. | |
| 3. Reversing starter or contactor operation | 3. Ensure correct configuration of starter or contactor. |
#1. Industrial Machinery
Electric Motors power a vast range of industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, and machine tools. They provide reliable and efficient mechanical motion for manufacturing processes.
#2. HVACR Systems
Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning , and Refrigeration (HVACR) systems use electric motors to drive fans and blowers for air circulation, refrigeration compressors for cooling, and pumps for fluid circulation in heating and cooling systems.
#3. Transportation
Electric motors are crucial in various modes of transportation:
3.1 Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs use electric motors for propulsion, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to internal combustion engines.
3.2 Trains and Locomotives: Electric motors drive the wheels of electric trains and locomotives, providing efficient and reliable transportation solutions.
3.3 Shipping and Logistics
Cargo handling equipment in ports and warehouses, such as cranes, forklifts, and conveyor systems, rely on electric motors for material handling and transportation.
#4. Mining and Construction
In mining and construction equipment, Electric Motors power conveyor belts, crushers, drilling rigs, pumps, and excavators, contributing to efficient material handling and site operations.
#5. Robotics and Automation
Electric motors play a critical role in robotics and automation systems by providing precise motion control for robotic arms, automated assembly lines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
#6. Agricultural Equipment
Agricultural machinery such as irrigation pumps, grain conveyors, and harvesting equipment use electric motors, which can improve efficiency and productivity in farming operations.
#7. Medical Equipment
Medical devices such as MRI machines, ventilators, and surgical tools rely on electric motors for precision and reliability in their operation.
#8. Steel and Metal Processing
Steel mills and metal fabrication facilities use electric motors to power rolling mills, cutters, grinders, and metal forming machines for processing raw materials into finished metal products.

Cooling Tower

Water Pump

CRH Train

Conveyor

Food Machinery

Automation

Agriculture
Medical
| Model | Rated power | Voltage | No load speed(rpm/min) | Pole | Rated Torque(N.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YE4-100L-2-3KW | 3KW | 380V | 2860 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-112M-2-4KW | 4KW | 380V | 2880 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-132S1-2-5.5KW | 5.5KW | 380V | 2900 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-132S2-2-7.5KW | 7.5KW | 380V | 2900 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-160M1-2-11KW | 11KW | 380V | 2930 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-160M2-2-15KW | 15KW | 380V | 2930 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-160L-2-18.5KW | 18.5KW | 380V | 2930 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-180M-2-22KW | 22KW | 380V | 2940 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-200L1-2-30KW | 30KW | 380V | 2950 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-200L2-2-37KW | 37KW | 380V | 2950 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-225M-2-45KW | 45KW | 380V | 2960 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-250M-2-55KW | 55KW | 380V | 2965 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-280S-2-75KW | 75KW | 380V | 2970 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-280M-2-90KW | 90KW | 380V | 2970 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-315S-2-110KW | 110KW | 380V | 2975 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-315M-2-132KW | 132KW | 380V | 2975 | 2 | 2.3 |
| YE4-315L1-2-160KW | 160KW | 380V | 2975 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-315L2-2-200KW | 200KW | 380V | 2975 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-355M1-2-220KW | 220KW | 380V | 2980 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-355M2-2-250KW | 250KW | 380V | 2980 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-355L1-2-280KW | 280KW | 380V | 2980 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-355L2-2-315KW | 315KW | 380V | 2980 | 2 | 2.2 |
| YE4-355L3-2-355KW | 355KW | 380V | 2980 | 2 | 2.2 |
| Model | Rated power | Voltage | No load speed(rpm/min) | Pole | Rated Torque(N.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YE5-100L1-4-2.2KW | 2.2KW | 380V | 1410 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-100L2-4-3KW | 3KW | 380V | 1410 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-112M-4-4KW | 4KW | 380V | 1435 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-132S-4-5.5KW | 5.5KW | 380V | 1440 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-132M-4-7.5KW | 7.5KW | 380V | 1440 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-160M-4-11KW | 11KW | 380V | 1460 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-160L-4-15KW | 15KW | 380V | 1460 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-180M-4-18.5KW | 18.5KW | 380V | 1470 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-180L-4-22KW | 22KW | 380V | 1470 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-200L-4-30KW | 30KW | 380V | 1470 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-225S-4-37KW | 37KW | 380V | 1475 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-225M-4-45KW | 45KW | 380V | 1475 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-250M-4-55KW | 55KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-280S-4-75KW | 75KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-280M-4-90KW | 90KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.3 |
| YE5-315S-4-110KW | 110KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-315M-4-132KW | 132KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-315L1-4-160KW | 160KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-315L2-4-185KW | 185KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-315L3-4-200KW | 200KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355M1-4-220KW | 220KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355M2-4-250KW | 250KW | 380V | 1490 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355L1-4-280KW | 280KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355L2-4-315KW | 315KW | 380V | 1490 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355L3-4-355KW | 355KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| YE5-355L4-4-400KW | 400KW | 380V | 1480 | 4 | 2.2 |
| Model | Rated Power | Voltage | No load speed(rpm/min) | Pole | Rated Torque (N.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YE4-112M-6-2.2KW | 2.2KW | 380V | 935 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-132S-6-3KW | 3KW | 380V | 960 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-132M1-6-4KW | 4KW | 380V | 960 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-132M2-6-5.5KW | 5.5KW | 380V | 960 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-160M-6-7.5KW | 7.5KW | 380V | 970 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-160L-6-11KW | 11KW | 380V | 970 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-180L-6-15KW | 15KW | 380V | 970 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-200L1-6-18.5KW | 18.5KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-200L2-6-22KW | 22KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-225M-6-30KW | 30KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-250M-6-37KW | 37KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2.1 |
| YE4-280S-6-45KW | 45KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-280M-6-55KW | 55KW | 380V | 980 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-315S-6-75KW | 75KW | 380V | 985 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-315M-6-90KW | 90KW | 380V | 985 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-315L1-6-110KW | 110KW | 380V | 985 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-315L2-6-132KW | 132KW | 380V | 985 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355M1-6-160KW | 160KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355M2-6-185KW | 185KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355M3-6-200KW | 200KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355L1-6-220KW | 220KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355L2-6-250KW | 250KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355L3-6-280KW | 280KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| YE4-355L4-6-315KW | 315KW | 380V | 990 | 6 | 2 |
| Model | Rated power | Voltage | No load speed(rpm/min) | Pole | Rated Torque(N.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YE3-132M-8-3KW | 3KW | 380V | 705 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-160M1-8-4KW | 4KW | 380V | 720 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-160M2-8-5.5KW | 5.5KW | 380V | 720 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-160L-8-7.5KW | 7.5KW | 380V | 720 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-180L-8-11KW | 11KW | 380V | 730 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-200L-8-15KW | 15KW | 380V | 730 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-225S-8-18.5KW | 18.5KW | 380V | 730 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-225M-8-22KW | 22KW | 380V | 730 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-250M-8-30KW | 30KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-280S-8-37KW | 37KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-280M-8-45KW | 45KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-315S-8-55KW | 55KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-315M-8-75KW | 75KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-315L1-8-90KW | 90KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-315L2-8-110KW | 110KW | 380V | 735 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355M1-8-132KW | 132KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355M2-8-160KW | 160KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355L1-8-185KW | 185KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355L-8-200KW | 200KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355L3-8-220KW | 220KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
| YE3-355L4-8-250KW | 250KW | 380V | 740 | 8 | 2 |
#1. Motor Information
Motor Nameplate Data
Verify Motor type, horsepower (HP), voltage, current rating, speed, and frame size against application requirements.

#2. Mechanical Inspection
2.1 Physical Condition
Inspect any damage, corrosion, or wear on motor housing, cooling fins, and mounting base.
2.2 Shaft Alignment
Check shaft alignment with connected equipment (pumps, fans,etc) to prevent excessive bearing wear.
2.3 Bearing Condition
Check bearings for smooth operation, listen for unusual noise or vibration.
2.4 Cooling System
Ensure cooling fan and air vents are clean and unobstructed for optimal heat dissipation.

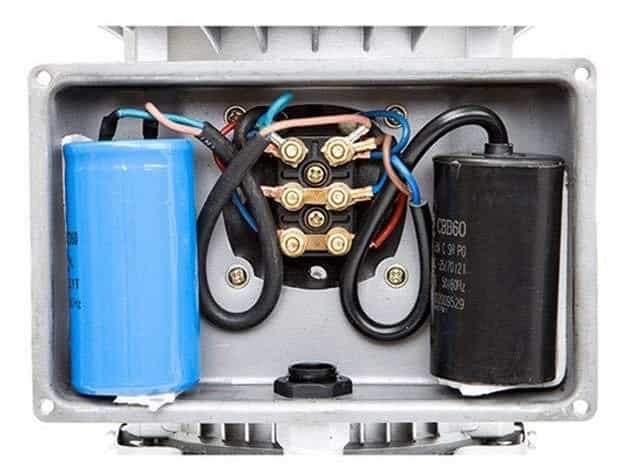
#3. Electrical Inspection
3.1 Electrical Connections
Inspect terminal connections for tightness and if any overheating.
3.2 Insulation Resistance
Test Motor windings for insulation resistance using a megohmmeter (megger).
3.3 Voltage and Current
Measure operating voltage and current to ensure they are within motor specifications.
3.4 Motor Starters and Controls
Check operation of motor starters, contactors, and overload relays for proper function.
#4. Operational Testing
4.1 Motor Start-Up
Verify smooth Motor start-up and absence of abnormal noise or vibration.
4.2 Load Test
Apply rated load (if possible) to confirm motor performance under normal operating conditions.
4.3 Speed Verification
Measure motor speed using a tachometer to ensure it matches the rated speed.
4.4 Efficiency Check
Calculate motor efficiency by comparing input power (voltage x current) with output mechanical power.

#5. Safety and Compliance
5.1 Safety Measures
Ensure all safety guards, covers, and labels are intact and compliant with safety standards.
5.2 Environmental Considerations
Verify motor installation meets environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.) specified by manufacturer.
#6. Maintenance and Documentation
6.1 Maintenance History
Review maintenance records and service history for the motor.
6.2 Documentation
Keep detailed records of inspection findings, test results, and any corrective actions taken.

Cable Connection

Superior Bearing

Copper Coil

Precision Rotor

Silicon Steel

High Precision Keyway

Matte Paint Finish

Excellent Cooling Cover

Features:
#1. Enclosure Design: Enclosures made of heavy-duty materials such as cast iron or aluminum.
#2. Sealed Construction: Motor enclosure are tightly sealed to prevent the ingress of flammable gases or dust.
#3. Special Venting: Has flame arrestors or pressure-relief mechanisms, which prevent external flames or gases from entering the motor while allowing safe venting of internal pressure.
#4. Non-Sparking Components: Use Non-ferrous metals and special alloys to minimize the risk of sparking during motor operation.

Features:
#1. High Efficiency: YE1/YE2/YE3/YE4 high efficiency motor.
#2. Sturdy Construction: High-quality cast iron or aluminum alloy frame.
#3. Low Noise and Vibration: Ensure smooth and stable performance.
#4. Class F Insulation: Provide high thermal resistance and reliability.
#5. IP55 Protection Rating: Make the motor dust-tight and protect against water jets from any direction.

Features:
#1. Synchronization with AC Power Supply
#2. Precise Speed Control
#3. Power Factor Correction
#4. No Slip
#5. Stable Operation at Variable Loads
#6. Low Noise and Vibration
#7.Wide Range of Sizes and Ratings

Features:
#1. High Energy Efficiency and Precision: IE1 (Standard Efficiency), IE2/IE3 (High Efficiency), or IE4 (Premium Efficiency).
#2. Premium Materials and Construction: High-grade steel for the stator and rotor
#3. Optimal Design for Performance: Has advanced electromagnetic configurations, precision windings to enhance performance, compact and lightweight.
#4. Variable Speed: Can adjust motor speeds to match varying load requirements.
#5. Fast Response Time: Quickly respond to control signals, making them suitable for dynamic applications with rapid changes in load or position.

Features:
#1. High Torque Output: Can produce high torque at low speed, ideal for heavy-duty applications required strong mechanical force.
#2. Precision and Control: Offer excellent control over speed and position, allowing for smooth and accurate operation.
#3. Robust Construction: Withstand harsh operating conditions and heavy loads, ensure durability and long service life.
#4. Direct Drive Options: Eliminate the need for intermediate gears and reduce complexity.
#5. Application: Conveyors / Mixers and Agitators / Cranes and Hoists / Mining Equipments/ Water Treatments, etc

Features:
#1. CE Marking and ISO Certification: Meet EU and requirements for most countries.
#2. Low Noise and Vibration: Ensure smooth and stable performance.
#3. Compliance with International Standards: Meet standard (IEC, NEMA) to ensure product quality.
#4. Easy Installation and Maintenance: Minimize downtime and reduce overall operating costs.
#5. VFD means “Variable Frequency Drive”
Frequently Asked Questions About Our Electric Motor
Single-phase motors operate on a single alternating current (AC) phase and are commonly used in residential applications (e.g., household appliances). Three-phase motors use three alternating currents and are more efficient and suitable for industrial and commercial applications due to smoother operation and higher power output.
To improve energy efficiency:
Speedway is committed to quality across all aspects of our business – our people, processes and products. We call this ‘the SPEEDWAY standard’.
We welcome any sample order before big quantity purchase, that means 1pc is acceptable. More than 10pcs we will give discount.
We have own factory to produce the main electric motor products, but we also do trading for other related products because we have resource to supply good quality and service.
Yes,we have 5 senior engineers, 12 professional r & D team, 75 professional production personnel.
We support payment through wire transfer, like T/T, L/C, Western Union. Also accpet Paypal payment for sample piece order.
For sure. You can send us your logo, package or panel design, we will give you the final satisfied solution accordingly without additional cost !
Use the formula: Efficiency (%)=(Output Power / Input Power) ×100
Yes, electric motors can use in hazardous locations (e.g., Class I, Division 1 or 2). These motors are built with explosion-proof enclosures, special seals, and non-sparking components to prevent ignition of flammable gases, vapors, or dust in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Steps include:
Partner with us to increase your brand reputation, get an impressive experience for your clients to remember you lifelong, and help you stand out in the competitive market !