Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial in cold room conditions where workers are exposed to extremely low temperatures and potentially hazardous conditions.
Ensure the safety and well-being of personnel in these settings requires the proper use of special design to protect against cold stress, injury, and other risks.
This article explores the essential PPE for cold room, highlight its importance in maintaining a safe and efficient workplace.
Unique Nature of Cold Room Work Condition
1.Low Temperature and High Humidity
Temperature range: Typically between -18°C (food cold room) and -60°C (ultra-low-temperature medical cold room), with extreme cold causing rapid body heat loss.
Humidity impact: Moisture inside cold room condenses into frost, increasing slip hazards, while dampness intensifies perceived coldness.
Prolonged exposure risks:
Over 30 minutes: Risk of frostbite (fingers, toes, ears, nose, and other extremities).
Over 1 hour: Hypothermia symptoms (confusion, abnormal heart rate).
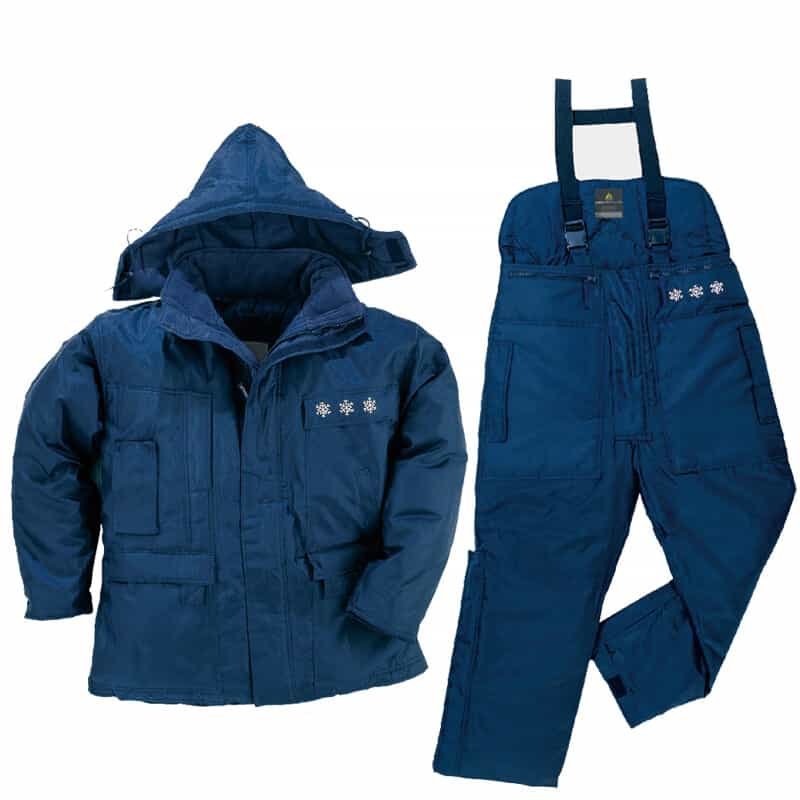

2.Core Value of Cold Room PPE
Specialized vs. ordinary warmth:
Regular clothing only focus on warmth; cold room PPE must integrate windproofing, waterproofing, abrasion resistance, and anti-static properties.
Mandatory compliance with international safety standards (e.g., EN 342 for cold-protective clothing), ensure materials remain flexible in extreme cold.
Cold Room PPE Core Function
1.Body Temperature Keep
Multi-layer insulation: Outer windproof layer, middle warmth layer, and inner moisture-wicking layer minimize heat loss.
Key data: Unprotected skin in -30°C drops to 0°C within 10 minutes; PPE extends safe exposure to over 2 hours.
2.Physical Protection
Frostbite prevention: Full coverage of exposed skin (e.g., jumpsuits + neck guards + face masks).
Anti-slip design: Boot soles use deep-tread rubber or polyurethane (PU) with a friction coefficient ≥0.3 (ASTM F2913 standard).
3.Safety Assurance
High visibility: Reflective strips compliant with ISO 20471, visible from ≥200 meters in dim conditions.
Anti-static function: Surface resistance ≤10⁹Ω (EN 1149 standard), prevent sparks from igniting volatile gases (e.g., ammonia refrigerants).
4.Efficiency Enhancement
Lightweight design: Premium cold room jackets weigh <1.5 kg to reduce fatigue.
Joint flexibility: Elbow/knee areas use 3D tailoring or elastic fabrics for unrestricted movement during lifting/bending.
Cold Room PPE Classification
1.Body Protection
Cold room jackets/jumpsuits:
Outer material: 500D nylon + PU coating (waterproof rating ≥5000mm) to block frost penetration.
Insulation: Synthetic down alternatives (30% warmer than natural down in damp conditions).
Sealing: Double zippers + windproof flaps; elastic cuffs/hem.
Warm inner layers: Wool (natural antibacterial) or Polartec® Power Dry (moisture-wicking); avoid cotton (retains sweat and freezes).
2.Head & Face Protection
Cold-proof hats: Full ear coverage with fleece/thermal lining; some include Bluetooth slots for communication.
Face masks/neck guards: Neoprene (resistant to -40°C) to reduce direct inhalation of cold air.
3.Hand Protection
Low-temperature gloves:
Layered: Waterproof leather outer (anti-cut) + aerogel insulation (2mm thickness, 0.015W/m·K conductivity) + cashmere lining.
Dexterity: EN 388-certified for grip retention.
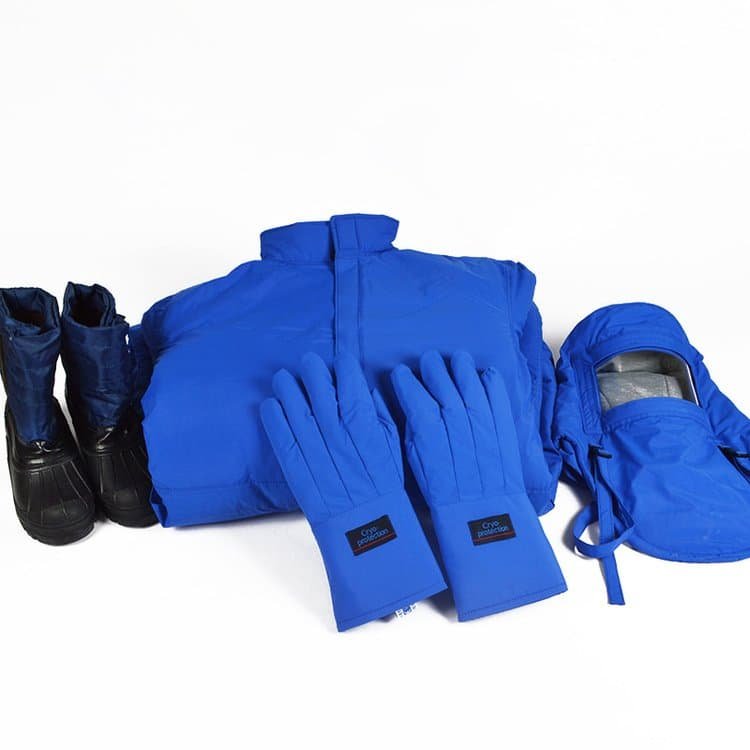

4.Foot Protection
Anti-slip boots:
Vibram® Arctic Grip soles (elastic even at -50°C); removable wool insoles + steel toes (EN ISO 20345 compliant).
5.Respiratory Protection (Special Request)
Heated masks: USB-powered micro-heating wires maintain inhaled air at ≥10°C.
6.Accessories
Battery-heated vests:
8-hour lithium battery; 40°C/50°C/60°C settings.
UL 1642-certified for battery safety, prevent overheating or short circuit.
Key Performance & Selection Criteria
1.Temperature Adaptability
Tier 1: -20°C to -30°C (food cold room).
Tier 2: -30°C to -50°C (medical cold room).
Tier 3: <-50°C (scientific ultra-low temp cold room).
2.Material Comparison
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Down | Best warmth (800+ fill power) | Loses 80% warmth when wet |
| Primaloft® | Stable in dampness | 20% costlier than down |
| Aerogel | Ultra-thin (≤3mm) | High cost (≥US$100/m²) |
3.Safety Certifications
EN 342: EU anti cold clothing standards; Full-body thermal insulation ≥0.5 clo (1 clo = 0.155m²·°C/W).
ISO 20345: Safety footwear (200J impact resistance, 15kN compression).
Proper Usage Guidelines
1.Wear Sequence (-30°C Example)
Step 1: Moisture-wicking underwears (avoid cotton).
Step 2: Mid-layer fleece/light down.
Step 3: Jumpsuit (fully zipped; check seals).
Step 4: Boots (pants over shafts), gloves (5cm sleeve overlap), neck/face guards.
2.Dynamic Adjustments
Sweat management: Ventilate by unzipping outer layers while keeping inner layers dry.
Tool: Use shoulder/thigh-mounted holders to avoid waist restrictions.
Precautions
1.Critical Errors
Metal-framed glasses: Risk of skin adhesion at -50°C → Use polycarbonate goggles/contacts.
2.Health Monitor
Frostbite signs: Whitened/hardened skin, numbness → Exit immediately; rewarm with 40°C water (no rubbing!).
3.Maintenance Errors
Washing aerogel gloves → Causes the insulation layer to break, 70% insulation loss → Wipe exterior only; hand-wash linings.
Maintenance & Care
1.Cleaning Frequency
High use: Clean outer weekly, inner monthly.
Low use: Full clean quarterly.
2.Drying Tips
Avoid heat (>40°C damages PU coatings).
Restore loft: Beat insulation with tennis balls.
3.Lifetime Indicators
Replace if waterproofing fails (water no longer beads) or boot treads <2mm.
Application & Cases
1.Medical Cold Room (-70°C)
Requirements: Protective clothing must pass ISO 13485 medical device certification to prevent material debris from contaminating medicines.
Solutions: Use anti-static + sterile suits,and positive-pressure respirators.
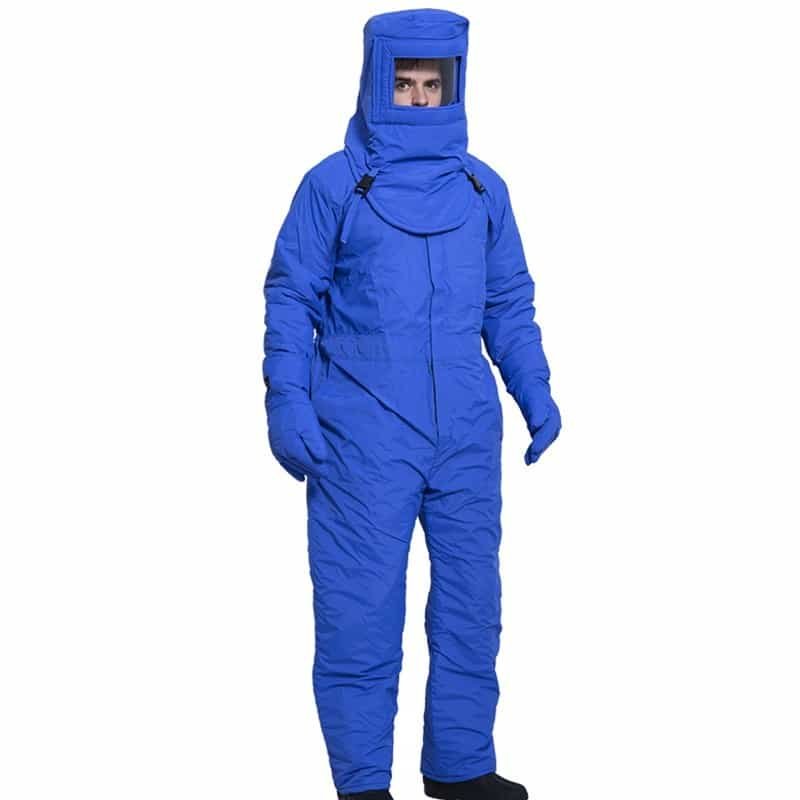

2.Logistics Case
Issue: 30% efficiency drop due to rigid gloves → Solution: Hestra Ergo Grip gloves boosted efficiency by 22%.
Future Trends
1.Smart Thermal Control
Graphene heating and AI body sensors (50% energy savings).
2.Bio-Based Materials
Mycelium-based coatings (biodegradable, waterproof).
3.Modular Design
Magnetic neck guards and detachable knee pads (5-second swaps).
Conclusion
Cold room PPE combines science and ergonomics, enhancing safety and efficiency through meticulous design.
Enterprises must select solutions tailored to specific conditions (temperature, humidity, tasks) and implement training/maintenance programs to build holistic safety systems for low temperature operations.
Any comments?
Welcome leave a message or repost.