In cold room, maintain an efficient, organized, and safe environment is essential to preserve product quality and ensure smooth operations. One often overlooked but critical aspect is the shelving system which used to store goods.
Choose the right cold room shelving can make a significant difference to maximize space, prevent product spoilage, and comply with safety regulations. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of cold room shelving, the various types available, and how to select the best shelving system for your specific needs.
Superior Cold Room Cooling
Cold Room Shelving Definition
Cold room shelving refers to special storage systems for use in low-temperature controlled environments, such as refrigerated or frozen storage areas. These shelvings are built to withstand the low temperatures and high humidity in cold rooms, while offering efficient space utilization, durability, and ease of cleaning, which is made from materials resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel , plastic, or zinc-plated metals, to ensure long-lasting performance in cold conditions. The primary goal is to store products safely while maintaining proper air circulation to preserve their quality.

Why Cold Room Shelving is Essential?
Maximize Storage Space
Efficient Use of Vertical Space: Cold room shelving allows to maximize use of vertical space, which is particularly important in environments where every square foot is valuable. Proper shelving systems enable better organization, so products can be stored in layers without taking up extra floor space.
Optimal Layouts: Shelving systems can tailor to fit the unique layout of a cold room, ensure no space goes unused. This is very important in smaller cold rooms where maximizing capacity is key to maintain efficiency.
Maintain Product Quality
Air Circulation: Cold room shelving, especially wire shelving, helps to promote air circulation around products, ensure consistent temperature distribution. This is critical for preventing hotspots, where products may freeze or spoil due to uneven cooling.
Prevents Product Damage: By organizing items on shelving rather than stacking them on the floor, can reduce the risk of product damage. Shelving helps to keep products off the cold floor, avoiding condensation and possible contamination.
Support Hygiene and Food Safety Standard
Elevated Storage: Cold room shelving keeps products elevated off the ground, reduce risk of contamination from the floor. This helps meet hygiene standards, especially in food storage where maintaining cleanliness is critical.
Easy to Clean: The materials used for cold room shelving, such as stainless steel and zinc plated, are easy cleaning and sanitation. Regular cleaning prevents bacteria and mold from growing in the cold, damp and high humidity environment.
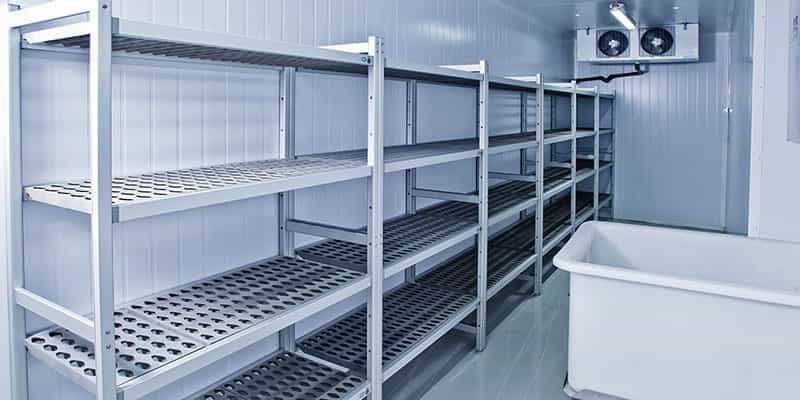

Types of Cold Room Shelving
(1).Wire Shelving
Wire shelving is a popular choice for cold room due to its open design, which allows for excellent air circulation. It’s made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or plastic-coated metal to withstand the damp, cold environment.
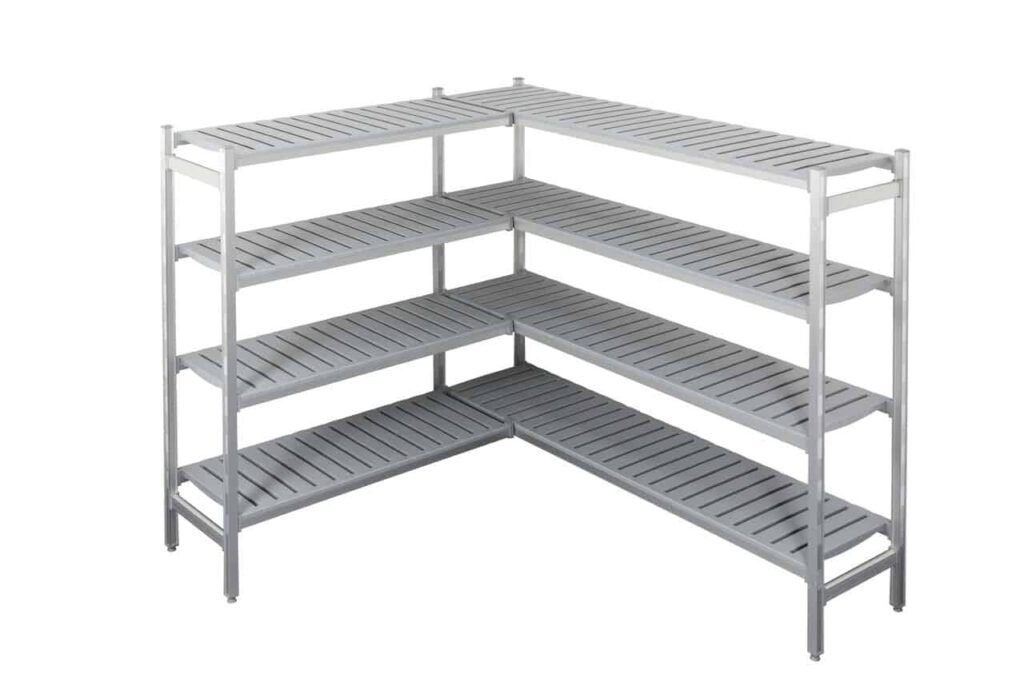

Advantages:
1. Airflow
Promote consistent air circulation, ensure uniform temperature distribution around preserved products.
2. Easy to Clean
The open structure is easy to clean and maintain, can meet hygiene standards.
3. Adjustable
Shelves can often adjust in height to accommodate different types of products, boxes or shapes.
Disadvantages:
1. Weight Limitations
Wire shelves aren’t suitable for very heavy loads as they are less sturdy than solid shelving.
Application: Food storage, pharmaceuticals, and general cold rooms which need airflow around products.
(2).Solid Shelving
Solid shelving is made from materials such as stainless steel or high-grade plastic. Unlike wire shelving, it features a flat, solid surface that prevents small items or liquids from dripping through the shelves.
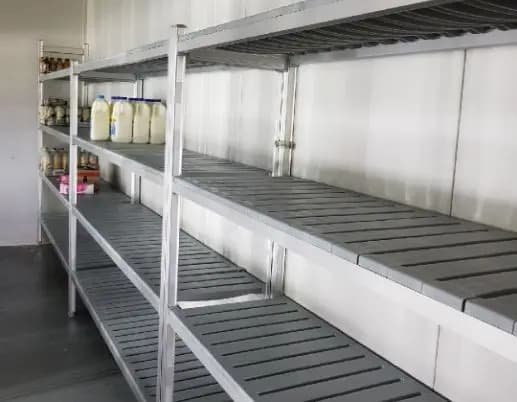

Advantages:
1. Durability
Solid shelves are highly durable and can handle heavier loads, suitable for storing large, heavy products.
2. Containment
Prevent spills or drips from reaching lower shelves, helping to contain liquids and prevent cross-contamination.
3. Hygienic
Provide a smooth surface that is easy to clean, ideal for maintaining strict hygiene requirements.
Disadvantages:
1.Limited Air Circulation
Unlike wire shelving, solid shelves can block air circulation, which may result in uneven cooling in certain areas of the cold room.
Application: Cold storage environments with heavy, bulky items, or where spill containment is a concern.
(3).Mobile Shelving
Mobile shelving systems can maximize space by allowing shelves to move along tracks. These units can move closer together or apart, eliminating the need for permanent aisles.
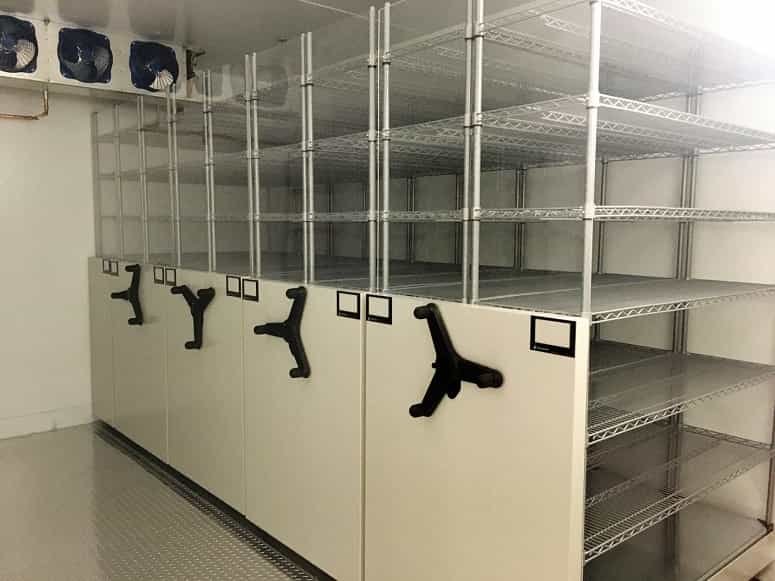

Advantages:
1. Maximize Space
Eliminates fixed aisles and allows more shelving n the same area, increasing storage volume.
2. Flexibility
Shelving units can be easily moved to create aisles only when needed, allowing for high-density storage.
3. Customized
Mobile shelving can customize to suit different types of products and cold storage needs.
Disadvantages:
1. Higher Cost
Mobile shelving systems are more expensive due to the complexity of the system.
2.Accessibility
Requires careful planning to access stored products, as only one aisle can be opened at a time.
Application: Cold room with limited space but high storage needs, or where maximizing storage efficiency is a priority.
(4).Drive-In Shelving
Drive-in shelving is suitable for high-density storage, where forklifts drive directly into the shelving system to place or retrieve pallets. This type of shelving is best for cold room where products stored and retrieved in large quantity.

Advantages:
1. High-Density Storage
Allows for large volumes of products to be stored in a compact area, making it ideal for bulk storage.
2. Space Efficiency
Maximizes storage space by eliminating aisles between shelves, allowing for more products stored in the same footprint.
Disadvantages:
1. Limited Accessibility
Drive-in systems operate on a “last in, first out” basis, meaning the products stored at the back of the system are harder to access.
2. Specialized Equipment Needed
Require forklifts or other equipment to access products, which will increase operational complexity.
Application: Warehouses with large quantity of uniform products, especially in food or beverage industries where items can be stored in bulk.
(5).Pallet Racking
Pallet racking is one of the most common cold room shelving systems used in large-scale warehouse. It can hold pallets of goods, offering easy access and strong support for heavy items.

Advantages:
1. Heavy-Duty
Can support heavy pallets, suitable for storing bulk items.
2. Organized Storage
Provides a systematic way to organize and store pallets, making inventory management easier.
3. Accessibility
Can be accessed with forklifts or pallet jacks, allowing for efficient loading and unloading.
Disadvantages:
1. Require Special Equipment
Often requires forklifts, so may not be ideal for all storage spaces.
Application: Large cold storage warehouses, distribution centers, and industries that store products on pallets, such as frozen food or beverages.
(6).Cantilever Shelving
Cantilever shelving used to store long, bulky items such as pipes, lumber, or other oversized materials. It consists of arms that extend out from a central support, allowing for open, unobstructed storage.
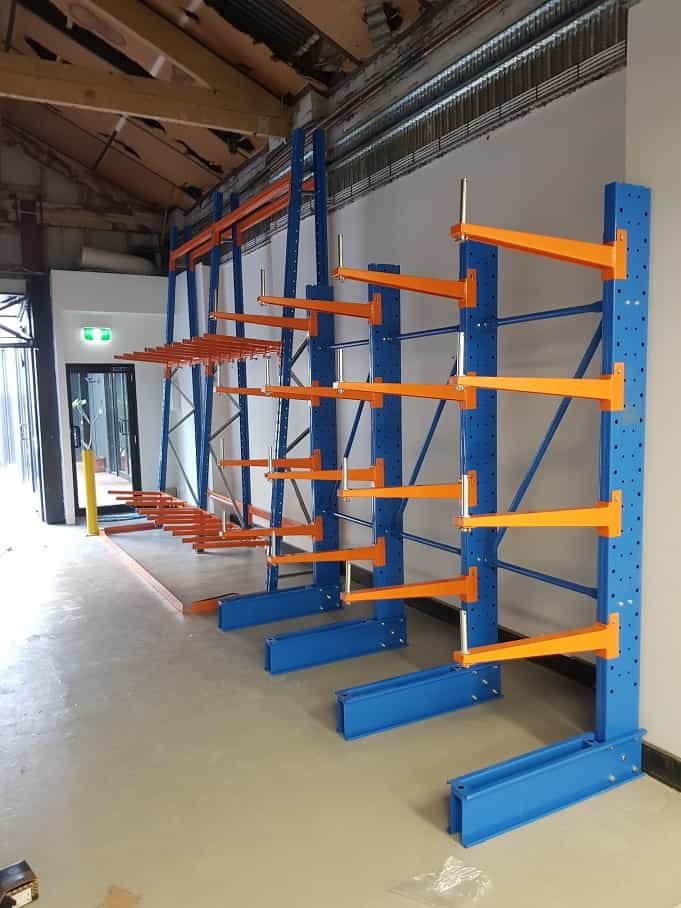

Advantages:
1. Perfect for Long Items
Ideal for items that don’t fit on standard shelving due to their length or irregular shape.
2. Flexible Storage
Cantilever systems can adjust to fit items of varying lengths.
Disadvantages:
1. Niche Use
This type of shelving isn’t suitable for most standard cold storage products.
Application: Cold rooms which handle long, bulky items like rolled products, construction materials, or large components.
(7).Modular Shelving
Modular shelving systems are customizable and can be easily expanded or reconfigured based on changing storage needs. They are often used for cold storage areas that require flexibility in product storage.
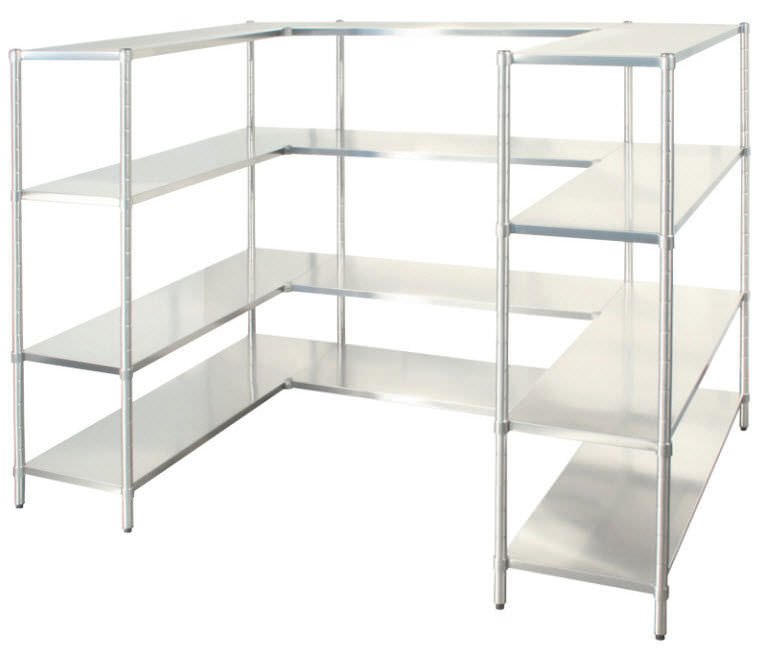

Advantages:
1. Adaptable
Adjust and reconfigure easily to meet changing storage needs or accommodate new product types.
2. Customizable
Available in various materials and designs to suit specific cold storage requirements.
Disadvantages:
1. Higher Initial Cost
Modular systems may be more expensive upfront but offer long-term value through flexibility.
Application: Cold rooms which need to adjust shelving configurations frequently, or those that store a wide variety of products.
Shelving Material Consideration
(1).Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is one of the most durable and hygienic materials used for cold room shelving, particularly well-suited for environments where cleanliness, resistance to corrosion, and strength are top priorities.

Stainless Steel
Application: Industries such as food storage, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare (due to its resilience in harsh, moist environments).
(2).Plastic-Coated Metal
Plastic-coated metal shelving combines the strength of metal with the corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning provided by a plastic coating. Normally, the metal frame is coated with polyethylene, PVC, or other types of plastic to protect against rust and moisture damage.

Plastic Coated Metal
Application:
1. Small to medium-sized cold rooms, especially for lighter products.
2. Food storage areas that require easy-to-clean shelves but don’t need the strength of stainless steel.
(3).Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel shelving is made by coating steel with a protective layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. This type of shelving is a cost-effective solution for cold storage environments that require sturdy shelves but may not need the full corrosion resistance of stainless steel.

Galvanized Steel
Application:
1. Large industrial cold rooms where strength and cost are more important than hygiene.
2. Cold storage areas that handle heavy products or pallets.
3. Clients looking for a balance between strength and cost without requiring the highest level of corrosion resistance.
Key Features to Look for When Choose Shelving
Load Capacity
Importance: Load capacity refers to the maximum weight a shelving unit can safely support without bending, warping, or collapsing. In cold storage environments, where products like food, pharmaceuticals, or industrial goods can be heavy, it’s essential that shelving systems are strong enough to handle substantial loads.
What to Look For: Shelving made from materials like stainless steel or heavy-duty galvanized steel. Check manufacturer’s weight specifications and ensure that the shelves can support the kind of loads you’ll be storing. It’s also important to ensure that load distribution is even across the shelves to avoid localized stress that can cause damage.
Temperature Resistance
Importance: Shelving used in cold room must be able to withstand the low temperatures and sometimes extreme conditions of refrigerated or frozen environments (<-40℃). Materials can warp, crack, or corrode in cold temperatures quickly, leading to frequent replacements and higher maintenance costs.
What to Look For: Opt materials that are suitable for cold or extremely cold environments, such as stainless steel, plastic-coated metal, or galvanized steel. These materials are resistant to temperature fluctuations, ensure the shelving won’t become brittle or unstable in cold condition. What’s more, some cold rooms may experience defrosting cycles or temperature changes, so the shelving should be able to handle these variations without weakening.
Ease of Cleaning
Importance: Hygiene is critical in cold rooms, particularly those handling food, pharmaceuticals, or other sensitive products. Shelves that are easy to clean help maintain cleanliness standards, prevent the growth of bacteria, mold, or mildew, and ensure the cold room complies with health regulations.
What to Look For: Shelving with smooth, non-porous surfaces, such as stainless steel or plastic-coated metal, is easier to clean and sanitize. Open-wire shelvings are also helpful because they allow for better airflow, which reduces moisture buildup that can lead to mold. Additionally, shelving that is easy to disassemble or move can simplify deep cleaning tasks.
Adjustability
Importance: Cold rooms often need to store variety of products with different sizes and weights. Adjustable shelving provides flexibility, allowing the storage system to adapt to changing inventory needs without the need for costly replacement or modification.
What to Look For: Look for shelving systems with adjustable shelves that can easily move up or down to accommodate different product sizes. Some shelving units come with modular designs, meaning they can expand or reconfigure as the storage needs evolve. Storage Systems which can fit with different types of shelves (solid, wire, pallet, etc.) offer even greater suitability.
Maintenance Tips for Cold Room Shelving
1. Regular Cleaning to Prevent Buildup of Frost, Dust, or Rust
What to Do—
Frequent Wiping: Wipe down shelves regularly to remove any frost, dust, or debris that may have accumulated. For shelving in freezer environments, use a cloth suitable for cold temperatures and a cleaning solution that won’t freeze or damage the shelf surface.
Defrost Cycles: If the cold room goes through defrost cycles, make sure to clean the shelving afterward to remove any collected water. This will prevent moisture from causing rust or corrosion on metal shelving.
Use Approved Cleaning Agents: When cleaning shelves, use products that are special for cold storage environments to avoid damage. Avoid harsh chemicals which may erode protective coatings on the shelves.
Deep Cleaning: Schedule periodic deep cleans where shelves are removed and cleaned thoroughly, ensure no moisture, mold, or rust is hidden in hard-to-reach areas.
Cold Room Shelving System
2. Routine Inspection for Structural Integrity and Corrosion
What to Do—
Inspect for Rust or Corrosion: Check metal shelves, particularly in high-humidity environments, for any signs of rust or corrosion. This is especially important for shelving made of galvanized steel or plastic-coated metal, as damage to the protective coating can expose the metal to moisture.
Check Welds and Joints: Examine the joints, welds, and connections between shelving units to ensure they are secure. Loose or damaged joints can cause shelves to become unstable, increasing the risk of collapse.
Evaluate Structural Integrity: Periodically test shelves’ load-bearing capacity to ensure they aren’t weakening under the weight of stored products. If you notice any bending or sagging, it may be time to replace the shelving or reduce the load.
Look for Signs of Damage: Look for cracks, chips, or any physical damage to the shelving units. Even minor damage can weaken the structural integrity of the shelves over time.
3. Proper Organization and Weight Distribution to Avoid Overloading Shelves
What to Do—
Follow Load Capacity Guideline: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s specified load limits for each shelf. If unsure, refer to the product manual or contact the manufacturer for guidance on how much weight each shelf can support.
Distribute Weight Evenly: Avoid placing all the heaviest items on a single shelf or in one area of the shelf. Instead, distribute the weight evenly across the entire surface to reduce strain on the shelving and prevent it from bowing or collapsing.
Organize for Efficiency: Keep heavier items on the lower shelves to prevent shelves from toppling over. This also makes it easier for workers to access heavier products without causing injury. Place lighter itesm on higher shelves.
Rearrange as Needed: As inventory changes, make adjustments to the weight distribution on the shelves to prevent long-term strain on any particular unit.
Conclusion
At last, select right cold room shelving involves understanding its definition, exploring different types, considering suitable materials, and evaluating key features like durability, load capacity, and ease of maintenance.
By choosing shelving that meets your specific needs, you can ensure efficient storage, optimal organization, and long-term reliability for your cold room.
Any comments?
Welcome leave a message or repost.